The Advantages of Water-Cooled Power Supply
By: Brian Lu/ MWUSA Technical Service Dept.
brian@meanwellusa.com
Based on different application, thermal dissipation methods can be different. Generally, natural convection, forced convection, and water cooling are common thermal dissipation methods and possess different thermal dissipation capabilities. Please refer to the following description of comparison based on different thermal dissipation methods.
- Comparison of heat transfer coefficient betweendifferent dissipation methods
| Heat dissipation method | Heat transfer coefficient (W/m2K) |
| Natural convection | 3-12 |
| Forced air convection | 10-100 |
| Water cooling | 3000-7000 |
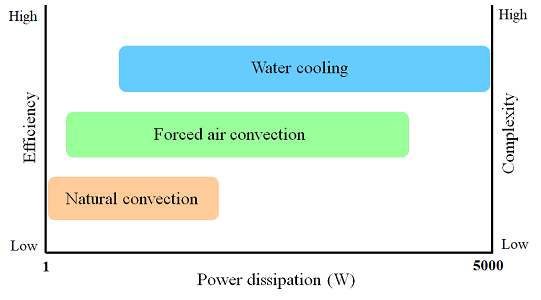
- Comparison of heat dissipation capability between different thermal dissipation methods
 |
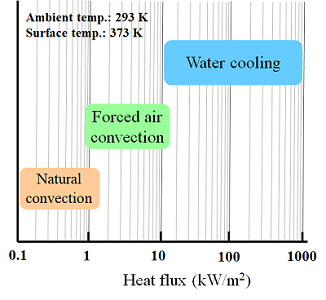 |
From the table and graph above mentioned, it is obvious that water cooling possesses higher thermal dissipation capabilities, but, higher cost on system mechanism design is expected. Comparison between three different thermal dissipation methods of SPS includes advantage, disadvantages and applications as shown in the table below.
| Advantages | Disadvantages | Applications | |
| Natural convection (Passive) |
• Widely available • Low Cost • No extra power consumption • No acoustic noise and vibrations, silent operation • Minimal maintenance • Simple construction, easy installation. |
• Low heat dissipation capability • Large heat dissipation area requirement • Strongly orientation dependence • Hard to control the efficiency of heat dissipation under different environmental conditions • Convection surfaces must be free from debris and corrosion |
• Low power density applications • No noise, vibration requirements, such as low power medical equipment, indoor lighting, home electronics, security, precision instruments, etc. |
| Forced air convection (Active) | • Lower thermal resistance for the same volume compared to passive thermal dissipation methods • Greater thermal dissipation capability compared with passive thermal dissipation methods • Customized cooling performance. |
• Short term reliability • Costly • Require regularly maintenance and replacements. • Foreign object debris such as dust • Acoustic noise and vibrations • Require an additional energy source for operation. |
• Medium to high power density applications • Systems with existing air flow • Normally used in Industrial equipment, information and communications, outdoor lighting, etc. |
| Water Cooling (Active) |
• Much greater heat dissipation capability • High thermal dissipation efficiency • No noise and vibration, quiet operation • Effective cooling with high ambient temperatures • Increase of SPS lifetime •Very wide operating temperature range |
• Complexity • Costly • Susceptibility to leaks • Require an additional external liquid chiller |
• High to ultra power density applications • Low profile applications • Require constant heat cycling equipment • Harsh environments • Mostly used in the high power industrial equipment such as industrial laser, charging station, etc. |
Convection cooled and forced-air cooled had been widely adopted in switching mode power supply designs and usually integrated into applications producing either less heat or low to mid-power range. Applications that produce high heat such as Fiber Laser needs to utilize water circulation (water-cooled) via a water chiller to dissipate the heat. Compact High Power (~10KW up) applications also use the water-cooled technique in order to reduce the overall form factor. Taking advantage of the preexist water chiller, the water-cooled power supply is the first choice for Laser and high-power compact design applications rather than convection or forced-air cooled power supply.
MEAN WELL first Water-cooled Power Supply, PHP-3500 series, is capable to output up 3,500W. Through active current sharing function, up to four units can be parallel to deliver up to 14,000W. With water-cooled capability, the PHP-3500 is suitable for Fiber Laser and compact high power applications that equipped with water chiller. Beside water-cooled, the PHP-3500 series can also be forced-air cooled by external fans to deliver full power for industrial automation application. However, water-cooled can effectively lower the internal components temperature of the power supply. The video below shows the PHP-3500-48 Power MOSFET and Capacitor temperature between water-cooled and force-air cooling.
In summary, the measured Power MOSFET and Capacitor temperatures are about 6~18°C lower when the PHP-3500-48 is used with water-cooled as compare to forced-air cooling. Therefore, Water-cooled technique not only provides better temperature to power supply internal components, and thus better reliability but also enable high power or Fiber Laser applications to be designed with smaller form factor along with the PHP-3500 series.
